Mettez-vous hors ligne avec l'application Player FM !
REBEL Core Cast 131.0 – Traumatic Arthrotomy
Manage episode 450809992 series 3381424
- Always suspect an open joint if there is a laceration, regardless of size, the lies over joint
- CT scan of the affected joint is widely considered to be the standard approach to evaluation but the saline load test may be useful in certain circumstances.
- Obtain emergency orthopedics consultation for all open joints and administer antibiotics and update tetanus in all patients
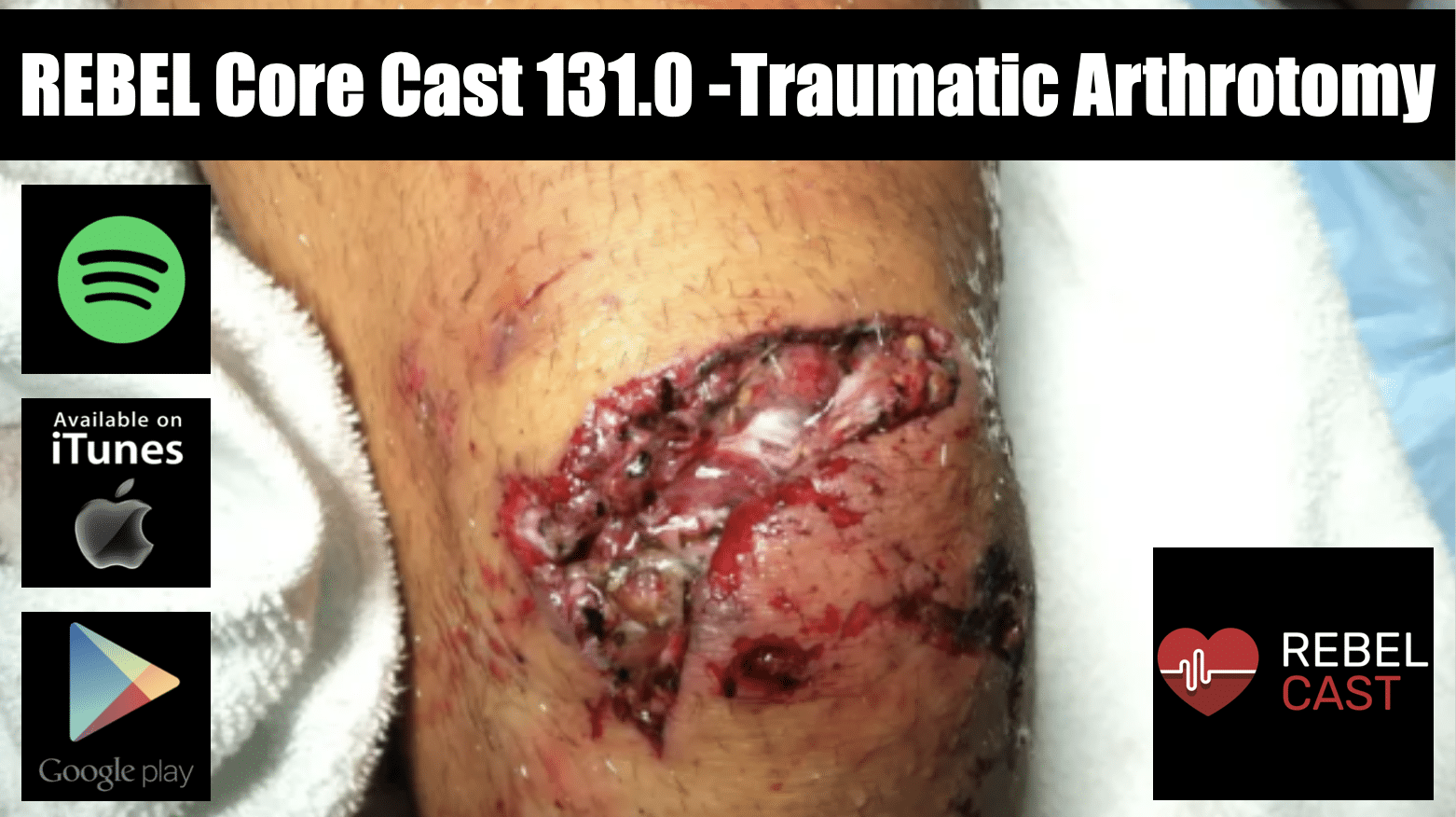
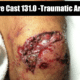
Definition: a deep laceration that extends into the joint capsule, exposing the intra-articular surface to the environment
- A laceration into the joint exposes the normally sterile intra-articular contents to external contamination
- Inoculation of the joint often results in septic arthritis
Physical Exam:
- Laceration over joint (can be variable in size)
- Local wound exploration may be sufficient in identifying the open joint
- Exam findings suspicious for joint capsule involvement:
-
- Air bubbles
- Extravasation of joint fluid – straw colored, viscous, sometimes oily in appearance
-
Diagnostic testing:
- Imaging:
- X-ray
- Limited ability to see air in joints but a reasonable first test
- CT scan
- Intra-articular air visualized on CT (Konda 2013)
- May be up to 100% sensitive for joint violation
- Study limited by small numbers, inclusion bias + inadequate gold standard
- May be considered the standard evaluation modality in many settings.
- Intra-articular air visualized on CT (Konda 2013)
- X-ray
- Saline load test
- Has mainly been supplanted by CT scan due to ease in obtaining, reported performance characteristics, consultant recommendation and difficulty in interpreting test.
- Useful if physical examination equivocal or plain radiographs non-diagnostic
- Technique (Video)
- Perform arthrocentesis of the joint with a large bore needle (18-20 gauge)
- Sterile saline is injected into the joint while passive movement is applied to the joint
- The laceration site is watched for saline extravasation indicating communication between the joint and external environment
-
- Sensitivity ranges from 34%-99% depending on the study, joint, and the amount of saline used to load the joint (Browning 2016)
- Methylene blue
- Aids in distinguishing a true positive from additional bleeding from the wound
- Recent studies suggest that the addition of methylene blue does not increase sensitivity if a sufficient amount of saline is used (Metzger 2012)
- Volume of fluid injected
- Varies depending on the joint in which you are injecting
- Higher volumes increase sensitivity but also increase pain for the patient
- Knee Joint (Keese 2007)
- 50 ml: Sensitivity of about 46%
- 194 ml: sensitivity of 95%
- Elbow Joint (Feathers 2011)
- 20 ml: Sensitivity of 86%
- 40 ml: Sensitivity of 95%
- Ankle Joint (Bariteau 2013)
- 7 ml: Sensitivity of 50%
- 30 ml: Sensitivity of 95%
ED Management:
- Reduce open fractures if present
- Irrigate grossly contaminated wounds in the ED
- Immobilize the joint to prevent further injury
- Obtain early orthopedic evaluation for joint exploration, and washout to be performed within 6-24 hours
- Tetanus prophylaxis
- Prophylactic antibiotics (best if given within 6 hours)
- Staph/strep coverage: 1st generation cephalosporin (i.e. cefazolin or cefuroxime)
- If risk factors for MRSA present, use agent with activity against MRSA (i.e. vancomycin)
- If significant soft tissue injury, add gram negative coverage like late generation cephalosporin, extended-spectrum penicillin, or aminoglycoside (i.e. gentamycin)
- If concern for fecal or clostridial infection, add high dose penicillin (i.e. zosyn)
- If seawater contamination and concern for vibrio vulnificus, add doxycycline
Post Peer Reviewed By: Salim R. Rezaie, MD (Twitter/X: @srrezaie)
The post REBEL Core Cast 131.0 – Traumatic Arthrotomy appeared first on REBEL EM - Emergency Medicine Blog.
29 episodes
Manage episode 450809992 series 3381424

- Always suspect an open joint if there is a laceration, regardless of size, the lies over joint
- CT scan of the affected joint is widely considered to be the standard approach to evaluation but the saline load test may be useful in certain circumstances.
- Obtain emergency orthopedics consultation for all open joints and administer antibiotics and update tetanus in all patients
Definition: a deep laceration that extends into the joint capsule, exposing the intra-articular surface to the environment
- A laceration into the joint exposes the normally sterile intra-articular contents to external contamination
- Inoculation of the joint often results in septic arthritis
Physical Exam:
- Laceration over joint (can be variable in size)
- Local wound exploration may be sufficient in identifying the open joint
- Exam findings suspicious for joint capsule involvement:
-
- Air bubbles
- Extravasation of joint fluid – straw colored, viscous, sometimes oily in appearance
-
Diagnostic testing:
- Imaging:
- X-ray
- Limited ability to see air in joints but a reasonable first test
- CT scan
- Intra-articular air visualized on CT (Konda 2013)
- May be up to 100% sensitive for joint violation
- Study limited by small numbers, inclusion bias + inadequate gold standard
- May be considered the standard evaluation modality in many settings.
- Intra-articular air visualized on CT (Konda 2013)
- X-ray
- Saline load test
- Has mainly been supplanted by CT scan due to ease in obtaining, reported performance characteristics, consultant recommendation and difficulty in interpreting test.
- Useful if physical examination equivocal or plain radiographs non-diagnostic
- Technique (Video)
- Perform arthrocentesis of the joint with a large bore needle (18-20 gauge)
- Sterile saline is injected into the joint while passive movement is applied to the joint
- The laceration site is watched for saline extravasation indicating communication between the joint and external environment
-
- Sensitivity ranges from 34%-99% depending on the study, joint, and the amount of saline used to load the joint (Browning 2016)
- Methylene blue
- Aids in distinguishing a true positive from additional bleeding from the wound
- Recent studies suggest that the addition of methylene blue does not increase sensitivity if a sufficient amount of saline is used (Metzger 2012)
- Volume of fluid injected
- Varies depending on the joint in which you are injecting
- Higher volumes increase sensitivity but also increase pain for the patient
- Knee Joint (Keese 2007)
- 50 ml: Sensitivity of about 46%
- 194 ml: sensitivity of 95%
- Elbow Joint (Feathers 2011)
- 20 ml: Sensitivity of 86%
- 40 ml: Sensitivity of 95%
- Ankle Joint (Bariteau 2013)
- 7 ml: Sensitivity of 50%
- 30 ml: Sensitivity of 95%
ED Management:
- Reduce open fractures if present
- Irrigate grossly contaminated wounds in the ED
- Immobilize the joint to prevent further injury
- Obtain early orthopedic evaluation for joint exploration, and washout to be performed within 6-24 hours
- Tetanus prophylaxis
- Prophylactic antibiotics (best if given within 6 hours)
- Staph/strep coverage: 1st generation cephalosporin (i.e. cefazolin or cefuroxime)
- If risk factors for MRSA present, use agent with activity against MRSA (i.e. vancomycin)
- If significant soft tissue injury, add gram negative coverage like late generation cephalosporin, extended-spectrum penicillin, or aminoglycoside (i.e. gentamycin)
- If concern for fecal or clostridial infection, add high dose penicillin (i.e. zosyn)
- If seawater contamination and concern for vibrio vulnificus, add doxycycline
Post Peer Reviewed By: Salim R. Rezaie, MD (Twitter/X: @srrezaie)
The post REBEL Core Cast 131.0 – Traumatic Arthrotomy appeared first on REBEL EM - Emergency Medicine Blog.
29 episodes
Tous les épisodes
×Bienvenue sur Lecteur FM!
Lecteur FM recherche sur Internet des podcasts de haute qualité que vous pourrez apprécier dès maintenant. C'est la meilleure application de podcast et fonctionne sur Android, iPhone et le Web. Inscrivez-vous pour synchroniser les abonnements sur tous les appareils.